As the world grapples with the pressing challenges of climate change and environmental degradation, the call for sustainable practices has transcended borders and industries. Among the key players in this global movement are banks—institutions traditionally seen as guardians of finance but now called to become champions of sustainability. In an era where stakeholders are increasingly prioritizing ethical investments and eco-friendly policies, the question looms large: Why must banks embrace sustainability without delay? This article explores the undeniable link between financial stability and environmental stewardship, urging these institutions to recognize their pivotal role in fostering a sustainable future. By delving into the potential repercussions of inaction and highlighting the opportunities that lie in green investments, we aim to illuminate the path for banks willing to evolve and lead in this critical juncture of history.
Embracing Green Finance as a Strategic Imperative
In an era defined by climate urgency and shifting consumer expectations, adopting a sustainable financial framework is no longer a mere option for banks; it is essential for long-term viability and success. Green finance enables financial institutions to align their portfolios with environmentally conscious investments, paving the way for a resilient economy. By directing funds towards renewable energy projects, sustainable agriculture, and green real estate, banks can mitigate risks associated with climate change while optimizing returns. This proactive stance not only addresses global challenges but also fosters a reputation for corporate responsibility that attracts eco-minded customers and investors alike.
Moreover, implementing environmentally friendly practices goes beyond compliance; it offers a competitive advantage in a rapidly evolving market. Financial institutions can leverage innovative financing solutions such as green bonds, sustainability-linked loans, and impact investing to diversify their offerings. By creating structured programs that reward sustainable initiatives, banks can encourage clients to adopt greener practices. The strategic integration of sustainability into the core mission of banking operations will not only position these institutions as market leaders but will also catalyze broader social change. Below is a simple overview of the potential benefits:
| Benefits | Description |
|---|---|
| Risk Management | Reduces exposure to climate-related risks. |
| Customer Loyalty | Attracts a growing base of environmentally conscious clients. |
| Regulatory Compliance | Meets emerging sustainability regulations and standards. |
| Positive Impact | Contributes to local and global sustainability goals. |

The Role of Banks in Promoting Sustainable Development Goals
Banks hold a pivotal position in driving progress towards sustainable development goals by channelling financial resources toward environmentally and socially responsible initiatives. Their ability to influence investment patterns means they can either support or inhibit sustainable practices across various sectors. By adopting policies that prioritize sustainable projects, banks can ensure that their lending practices contribute to positive outcomes such as reduced carbon footprints, improved community resilience, and a commitment to ethical business practices. Engaging with clients on sustainability can also unlock new business models and innovative solutions, fostering an ecosystem where sustainability is seen as a strategic advantage rather than merely a compliance requirement.
Furthermore, transparency in banking operations surrounding sustainable development is crucial for building trust and credibility. Banks can establish specific metrics and standards to monitor their performance in relation to social and environmental impacts. Establishing such benchmarks not only improves accountability but also motivates stakeholders to work towards common objectives. The following key actions exemplify how banks can integrate sustainability into their core operations:
- Incorporating ESG criteria: Invest in projects that align with environmental, social, and governance (ESG) standards.
- Green financing: Offer specialized loan products for renewable energy projects and sustainable businesses.
- Stakeholder engagement: Collaborate with communities and clients to co-create sustainable solutions.

Integrating Environmental Risk Into Financial Decision Making
Financial institutions are increasingly recognizing that traditional risk assessment models are insufficient in today’s dynamic landscape. By embedding environmental considerations into their financial decision-making processes, banks can not only mitigate potential losses associated with climate risks but also seize new opportunities that arise from the transition to a sustainable economy. Examples of environmental risks include natural disasters exacerbated by climate change, regulatory shifts governing emissions, and shifts in consumer preferences towards eco-friendly products. By proactively identifying these risks, banks can strengthen their portfolios and improve long-term resilience.
To effectively integrate environmental risk into their frameworks, financial institutions can adopt several key strategies:
- Assessment of ESG Factors: Continuously evaluate environmental, social, and governance (ESG) metrics when analyzing potential investment opportunities.
- Scenario Analysis: Implement scenario planning to understand how various environmental developments could impact financial performance over time.
- Collaboration with Stakeholders: Engage clients, investors, and regulatory bodies in conversations about sustainable practices and expectations.
Additionally, it is vital for banks to track their exposure to high-risk sectors heavily influenced by environmental factors. The table below illustrates this concept by providing examples of sectors with varying degrees of environmental risk exposure:
| Sector | Risk Exposure Level |
|---|---|
| Energy (Fossil Fuels) | High |
| Agriculture | Medium |
| Renewable Energy | Low |
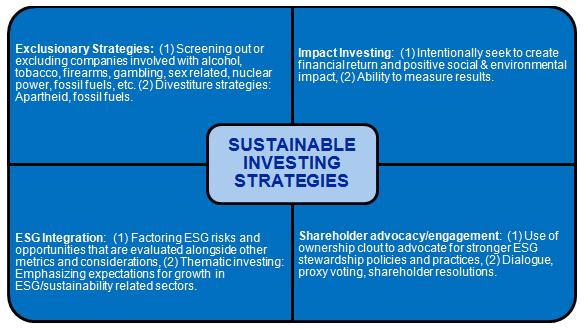
Building Resilience Through Sustainable Investment Strategies
In an era where climate change and social inequality pose significant risks to economic stability, banks have a unique opportunity to strengthen their operations and build long-term resilience through the integration of sustainable investment strategies. By redirecting capital flows towards eco-friendly initiatives and socially responsible enterprises, financial institutions can not only mitigate the risks associated with environmental degradation and social injustice but also capitalize on emerging market opportunities. This proactive approach will position banks as leaders in the transition toward a more sustainable economy, potentially increasing their competitive edge while ensuring compliance with evolving regulatory frameworks.
To effectively embrace this paradigm shift, banks should focus on several key strategies:
- Developing ESG Criteria: Incorporate environmental, social, and governance factors into investment assessments to guide decision-making.
- Engaging Stakeholders: Foster collaboration with clients, investors, and communities to enhance transparency and promote sustainable practices.
- Innovating Financial Products: Create green bonds and sustainability-linked loans that incentivize clients to pursue environmentally friendly projects.
- Investing in Technology: Leverage fintech solutions to track and report on sustainability metrics, enhancing accountability and measurement of impact.
This multi-faceted approach will not only safeguard financial stability but also contribute to the greater good, responding to the urgent demands of a changing world. As banks prioritize sustainability, they pave the way for a responsible financial ecosystem better equipped to face future challenges.
In Retrospect
In a world increasingly defined by the urgent calls for sustainability, banks find themselves at a pivotal crossroads. The imperative to embrace sustainable practices is not merely a trend; it is an opportunity to secure long-term viability and relevance in a rapidly evolving economic landscape. As stewards of capital and catalysts for economic growth, financial institutions have the power to drive meaningful change, influencing everything from environmental initiatives to social equity.
By integrating sustainability into their core strategies, banks can not only bolster their reputations but also enhance their operational resilience and foster the trust of a more environmentally-conscious clientele. The risks of inaction are significant, yet the prospects of adopting sustainable finance present a roadmap toward both profitability and responsibility.
The call to action is now. Delay in embracing sustainability could mean missing out on the very innovations and partnerships that are shaping the future of finance. As the narrative of banking evolves, let us recognize that sustainability is not just an ethical imperative but a strategic necessity. It is time for banks to step forward, pioneer a sustainable future, and, in doing so, unlock a wealth of lasting benefits for themselves, their stakeholders, and the planet. The journey toward sustainability awaits; the question is, who will lead the way?
