In an increasingly digital world, where the rapid evolution of technology intersects with the growing threats of cybercrime, the banking sector finds itself at a critical crossroads. As custodians of financial trust and vast troves of sensitive data, banks must not only defend against cyber threats but also cultivate a robust posture of resilience. Cyber resilience goes beyond mere defense; it encompasses an organization’s ability to prepare for, respond to, and recover from cyber incidents while maintaining essential operations. In this article, we will explore five essential steps that banks can take to build a strong foundation of cyber resilience—enabling them to adapt to an ever-changing landscape, safeguard their assets, and ultimately preserve the trust of their customers.
Fostering a Culture of Security Awareness Across Banking Teams
Creating a resilient banking environment hinges on cultivating a robust culture of security awareness among all team members. It is crucial that every employee, from front-line staff to executive leadership, is equipped with the knowledge and tools to recognize and mitigate potential cybersecurity threats. Regular training sessions, interactive workshops, and access to informative resources can help foster this awareness. Importantly, sharing real-world case studies and incident simulations can make the concept of security more tangible, encouraging proactive behavior in day-to-day operations.
Engaging employees can also be enhanced through initiatives that promote security as a shared responsibility. Here are some effective strategies to consider:
- Security Champions Program: Designate individuals within teams as security advocates to lead discussions and initiatives.
- Gamification and Competitions: Organize challenges that reward employees for identifying vulnerabilities or completing training modules.
- Open Communication Channels: Encourage team members to report suspicious activities without fear of repercussion.
- Regular Updates and Newsletters: Keep security at the forefront of everyone’s mind with ongoing communication that highlights new threats and policies.
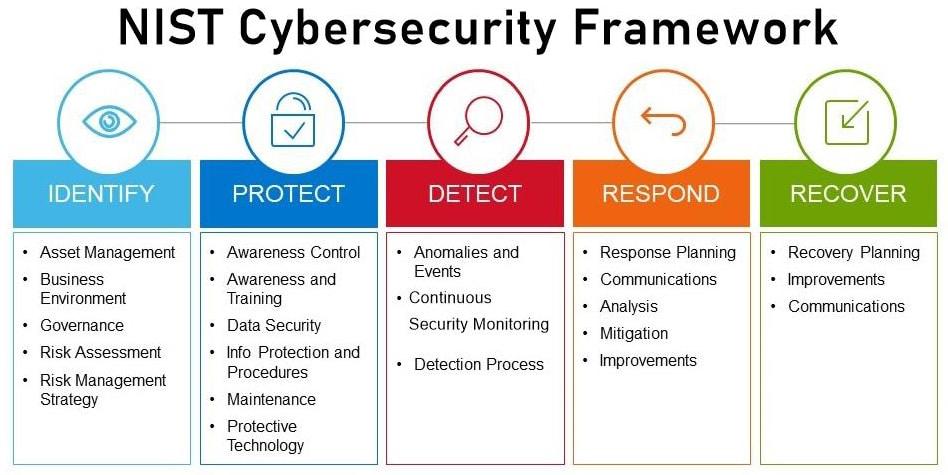
Implementing Robust Cyber Risk Assessment Frameworks
In the ever-evolving landscape of cyber threats, establishing a robust cyber risk assessment framework is crucial for financial institutions. This involves a systematic evaluation of potential vulnerabilities and the impact they could have on bank operations. The framework should incorporate multiple layers of assessment to understand both external and internal risks. Strategies may include:
- Asset Identification: Cataloging both digital and physical assets.
- Threat Modeling: Analyzing potential threats that could exploit vulnerabilities.
- Risk Analysis: Assessing the likelihood and impact of identified risks on operations.
- Control Assessment: Reviewing the effectiveness of existing controls.
- Reporting & Monitoring: Creating a continuous oversight mechanism for risk management.
To ensure the framework remains effective, a periodic review process must be integral to its design. Banks should utilize advanced technologies like AI-driven analytics and machine learning tools to enhance their risk assessment capabilities. By employing these innovations, institutions can automate data collection and analysis, providing a more comprehensive view of their risk landscape. Consider incorporating a visual representation of findings to facilitate quicker decision-making:
| Risk Type | Likelihood | Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Phishing Attacks | High | Critical |
| Data Breach | Medium | High |
| Ransomware | Low | Critical |
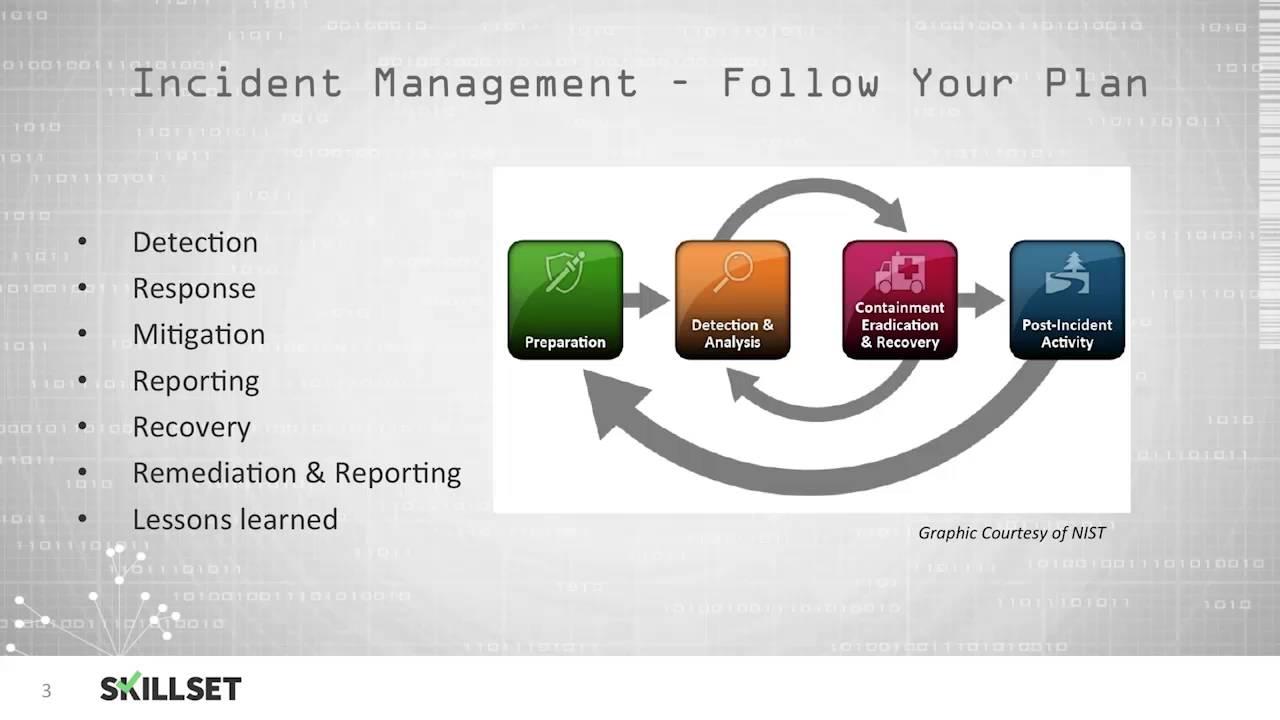
Strengthening Incident Response Plans Through Simulation and Training
To enhance cyber resilience, banks must not only develop robust incident response plans but also ensure that these plans are tested through realistic simulations and comprehensive training programs. Conducting regular tabletop exercises allows teams to engage in scenario-based discussions, identifying gaps and refining their strategies in a controlled environment. The use of realistic attack simulations empowers organizations to anticipate potential threats, while assessing both the technical and human elements of their response. The key areas to focus on during these simulations include:
- Communication Protocols: Ensuring all team members are aware of their roles and responsibilities.
- Decision-Making Processes: Testing the speed and effectiveness of decisions under pressure.
- Technical Response Capabilities: Evaluating the ability to contain breaches and recover operations quickly.
Incorporating continuous training into incident response strategies is essential for maintaining a cyber-ready workforce. By providing ongoing education and hands-on opportunities, banks can cultivate a culture of awareness and preparedness. Key components of an effective training program include:
| Training Component | Description |
|---|---|
| Phishing Simulations | Regular exercises to help employees recognize and report phishing attempts. |
| Incident Response Workshops | Interactive sessions that detail step-by-step response procedures. |
| Threat Intelligence Briefings | Updates on the latest threat landscapes and emerging risks. |
Leveraging Advanced Technologies for Enhanced Threat Detection and Prevention
As the threat landscape evolves, banks must embrace cutting-edge technologies to strengthen their security posture. Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) are revolutionizing threat detection by analyzing vast amounts of data quickly and accurately, identifying patterns that indicate potential breaches. These advanced systems can continuously learn from new data, allowing them to adapt to emerging threats and reduce false positives. By investing in these technologies, financial institutions can enhance their situational awareness and respond to incidents in real-time, ultimately minimizing the risk of data loss and reputational damage.
Moreover, integrating behavioral analytics into security frameworks provides an additional layer of defense. This approach monitors user behavior to establish a baseline, enabling the immediate identification of anomalies that may signify insider threats or compromised accounts. A robust combination of strategies can include:
- End-to-End Encryption: Safeguarding sensitive data during transmission.
- Threat Intelligence Sharing: Collaborating with other financial institutions to stay ahead of potential threats.
- Security Automation: Streamlining responses to incidents to improve reaction times.
To effectively manage these technologies, banks should also consider establishing a centralized Security Operations Center (SOC). This dedicated team will oversee security initiatives and ensure a swift response to any detected threats. By fostering a proactive security culture within their operations, banks can not only protect their assets but also instill confidence in their customers, demonstrating a commitment to safeguarding their financial information.
Insights and Conclusions
In the ever-evolving landscape of cybersecurity, the resilience of banks is more critical than ever. As we’ve explored, building cyber resilience is not just about fortifying defenses but embracing a comprehensive strategy that encompasses preparedness, response, and continuous improvement. By implementing these five essential steps, banks can transcend traditional security measures and foster an environment that not only withstands threats but also adapts to the dynamic challenges of the digital age.
As institutions navigate the complexities of modern finance, the commitment to cyber resilience will prove essential in safeguarding customer trust and sustaining organizational integrity. By prioritizing these strategies today, banks can secure their future against the uncertainties of tomorrow. After all, in a world where risks are ever-present, resilience isn’t merely an option—it is a necessity. With proactive measures in place, banks can rise to the challenge, setting a benchmark for security and reliability in the industry. The path to resilience is a journey, not a destination; and embarking on it today ensures that banks are prepared for whatever lies ahead.
